Software used by ACRI-IN experts
ACRI-IN uses a wide range of tools for use in its business, and has developed
or improved some of them as part of its R&D efforts. The software tools
currently used by ACRI-IN's scientific department include digital
calculation tools applied to fluid mechanics (WAVE PROPAGATION and
CURRENTS/SEDIMENTS) and structural mechanics (STRUCTURES/CIVIL ENGINEERING),
mapping tools (Geographic Information Systems - GIS), and finally CAD/CAM
(DESIGN/3D RENDERINGS).
-
WAVE/PROPAGATION
-
CURRENTS/SEDIMENTS
-
GIS
-
DESIGN/3D RENDERINGS
-
STRUCTURES/CIVIL ENGINEERING
-
REFDIF
REFDIF, initially
developed by Kirby and Dalrymple
(1983), is a wave propagation model
for irregular bottoms. It resolves
Berkoff's equation and takes into
account refraction, weakly
non-linear combined diffraction,
shoaling, interaction between swells
and ambient current, and even energy
dissipation.
SWAN
SWAN
(SimulatingWAvesNearshore)
is a third generation model that
generates a realistic estimate of
swell parameters in coastal areas,
in lakes and estuaries for given set
of wind, bathymetric and current
conditions. SWAN calculates the
random and irregular changes in
swells in coastal regions for deep,
intermediate and shallow water
depths under the effects of ambient
currents. The SWAN model takes into
account propagation (refraction and
diffraction) due to current and the
water depth, and shows the process
of generating swells by the wind,
dissipation due to surface wave
breaking, friction on the bottom,
bathymetric surge and non-linear
interactions between swells, using
specific state-of-the-art formulas.
SIMAC
SIMAC is a coastal
wave agitation model developed by
ACRI-IN. It evaluates agitation
close to a site by taking into
account the maximum undulating
effects caused by the seabed and the
presence of structures.
SIMAC-POSEIDON
SIMAC-POSEIDON is a
coastal wave agitation simulator
developed by ACRI-IN. It includes
several modules used, on one hand to
calculate the characteristics of a
wave propagating from open ocean
towards the coast over large
expanses, and on the other hand to
evaluate wave agitation near a site
by taking into account the maximum
undulating effects cause by the
seabed and the presence of
structures. This model follows the
propagation of the wave along the
entire length of its advance, even
when there are significant
diffraction phenomena.
-
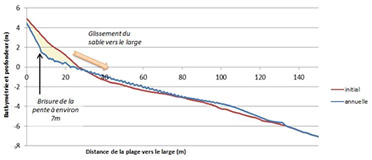
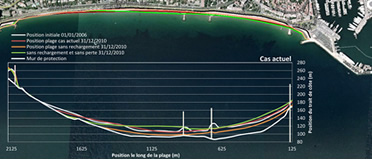
SBEACH
SBEACH is a model
that estimates the cross-sectional
profile of beaches during storms.
This software simulates sediment
transport caused by wave currents
and predicts beach erosion, berm
formation and movement, sedimentary
channels and berms under the
influence of strong storm surge and
variations in water level.
MEPBAY
MEPBAY is a
parabolic model which shows the
longitudinal profile of beaches
using equations by Hsu and Evans
(1989).
SMC
CMS, CMS, a coastal
management software called "Coastal
Modeling System", was developed by
the Ocean and Coastal Research Group
(GIOTTO) at the University of
Cantabrigian (Spain). Integrating
various interactive modules, it
performs hydrodynamic and
hydro-sedimentary studies. Its
propagation module, based on
REFDIF-SP software, resolves the
Berkoff equation. It is combined
with currents and sediments modules
that solve the flow equation and the
sediment conservation equation,
respectively.
DELFT3D
DELFT3D is a
completely integrated modeling
software in 2 and 3 dimensions,
developed by WL Delft Hydraulics
(The Netherlands). Delft3D is the
most effective 2D/3D environment
modeling software; it is also a
flexible software that simulates in
2D (both horizontally and
vertically) and 3 dimensions
currents, swells, water quality,
ecology, sediments transport,
morpho-dynamism, and processes the
interactions between these various
processes.
GENESIS
GENESIS (GENEralized
model for SimulatingShoreline
change) : code de calcul destiné à
la modélisation numérique de
l’évolution du littoral, développé
par le CERC.Ce modèle calcule
l’évolution de la position du trait
de côte en prenant en compte les
changements spatiaux et temporels du
transit littoral, des ouvrages tels
qu'épis, brise-lames, front de mer
et des apports et/ou prélèvements de
sédiments.Le modèle est à une
dimension, seul le trait de côte est
utilisé pour représenter l’évolution
du littoral. L’hypothèse de base est
que le profil se déplace par
translation sans modification de sa
forme pendant les processus
d’érosion ou d’engraissement => 1
point suffit pour déterminer la
position du trait de côte. Il est
alors faisable, moyennant
l’intégration des informations
tirées des mesures de terrain, des
simulations numériques complexes
mais limitées dans le temps et des
simulations physiques, de simuler
sur le long terme les évolutions
possibles du trait de côte
-
Qgis
Qgis : Management
tools, visualization, mapping to
query and analyze all data featuring
a spatial component.
-
AUTOCAD
AUTOCAD 2Dand/or 3D
computerized drawing software for
project study and design.
COVADIS
COVADIS : Autocad
application, for topography and
project take-offs.
3DS-MAX
3DS-MAX : 3D
animation, rendering and modeling
software for project development.
PHOTOSHOP
PHOTOSHOP : photo
retouching software
-
APILOG
APILOG :
Calculation of supports, beams,
piers, footings
STRUBAT(THONIER)
STRUBAT(THONIER) :
Structural calculations.
ROBOT STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
ROBOT STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS
2013 : Structural
finite element calculations and
expertise.
PROSHEET ( ARCELOR )
TALREN (TERRASOL)
TALREN (TERRASOL) :
Geotechnical structural stability
analysis (rubble mounds, earthen
dams, reinforced underground
structures, large anchored supports,
reinforced walls, etc.).
ARMACAD
ARMACAD : for
reinforcement schemes.
ACRI-IN has a state-of-the-art IT infrastructure. Read more